Marketing automation has fundamentally changed the way marketers do business. To be able to schedule cross-channel campaigns that deliver on time and on target frees up a lot of opportunity for marketers to focus on things like strategy, creative, and feedback loops. Campaigns run with fewer resources, still generating and nurturing leads. But unlike the flawless “set it and forget it” reliability of, say, a crock pot, automation has its risks.
With the advent of big data, media mix measurement and optimization has become a required staple in the marketer’s toolbox. Effectively media mix measurement and optimization is comprised of seven elements:
In Part 1 of this series, we discussed how organizational objectives may change the implementation of a media mix and optimization platform. And in Part 2, we talked about measuring the efficacy of your efforts. Now, let’s talk about collecting and normalizing consumer responses and order/sales data.
In Part 1 of this series, we discussed how organizational objectives may change the implementation of a media mix and optimization platform. Once the objectives have been set, it’s time to formulate a plan around how to measure the efficacy of your efforts.
With the advent of big data, media mix measurement and optimization have become a required staple in the marketer’s toolbox. Effectively, media mix measurement and optimization are comprised of seven elements:
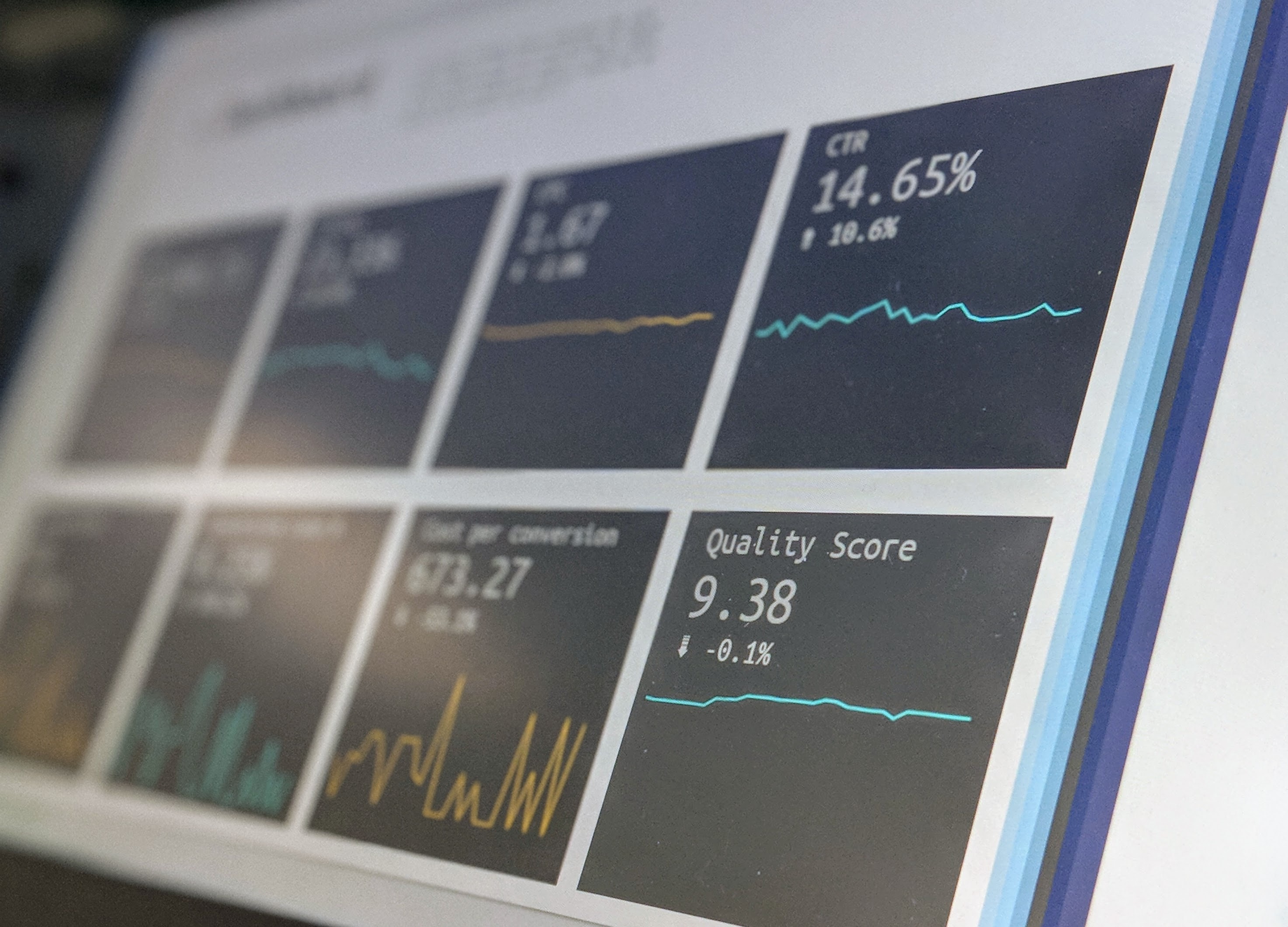
The events of 2020 have a long tail. As marketers enter 2021 with decreased marketing budgets, ROI is of increasing importance. Analytics and the ability to evaluate performance are key, especially as media mix is evolving. And it’s a great time for marketers to check in with their plans and confirm they are still looking at the right metrics.
Marketers use many different channels to reach customers, and they’re increasingly building omnichannel strategies that can follow and engage an audience on multiple different platforms. But when it comes to the marketing tools they use, too often these solutions are siloed from one another.
The appeal of automation makes sense: in a time where marketers are held to high standards and spread thin across an increased workload, anything you can set and forget is a welcome time saver. What companies didn’t predict, though, was how much time is attached to establishing automation. And while there are risks involved in automation’s perceived easy button, companies are still embracing it in droves. So how do marketers keep from blowing it?
More and more, consumers are bombarded with messages—from advertisements under the ice at a hockey game to mobile phone apps, or one of the thousands of other places ads are placed in today's media-rich environment. What stands out is how marketers are slowly taking up the concepts of offer optimization:
You have probably noticed hashtags during broadcasts, tweets streaming across the screen, second-screen applications where viewers can check in to watch a TV show together online and numerous other examples of the TV industry transforming itself into something more than a lean-back experience. The multi-billion dollar TV industry is fast undergoing a realignment from appointment television on the couch to a real-time, 24/7 entertainment anywhere business. So what can brands outside of the TV ecosystem learn from this?